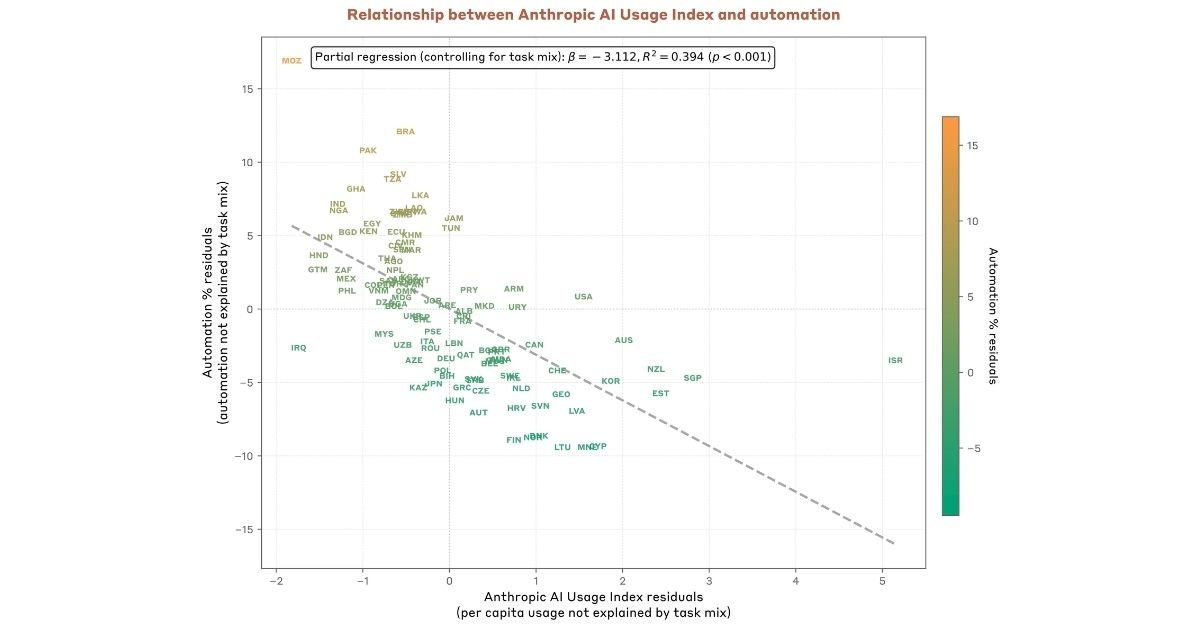
The Anthropic Economic Index Report has unveiled critical insights into the accelerating adoption of artificial intelligence in U.S. workplaces, revealing a surge in automation that poses risks of job displacement, particularly in sectors such as customer service and data entry.
According to the September 2025 edition, 42% of U.S. jobs now integrate AI for at least 30% of tasks, up significantly from prior years, with high-income regions like California and New York exhibiting elevated per capita usage.
Enterprises increasingly favor API integrations for systematic automation over chat-based interfaces, potentially amplifying productivity while heightening labor disruptions.
This data echoes JPMorgan’s forecasts of net employment gains amid short-term upheavals, akin to historical shifts like electrification, underscoring the Anthropic Economic Index Report’s role in illuminating AI’s transformative economic trajectory.
Background on the Anthropic Economic Index Report
Launched in February 2025 as part of Anthropic’s Economic Futures Program, the Anthropic Economic Index Report tracks AI’s integration into labor markets through anonymized analysis of millions of Claude.ai conversations via the Clio system.
Subsequent updates, including the May and September 2025 editions, have refined this methodology by mapping usage to occupational tasks from the U.S. Department of Labor’s O*NET database, distinguishing between augmentation, where AI enhances human efforts, and automation, which directly performs tasks.
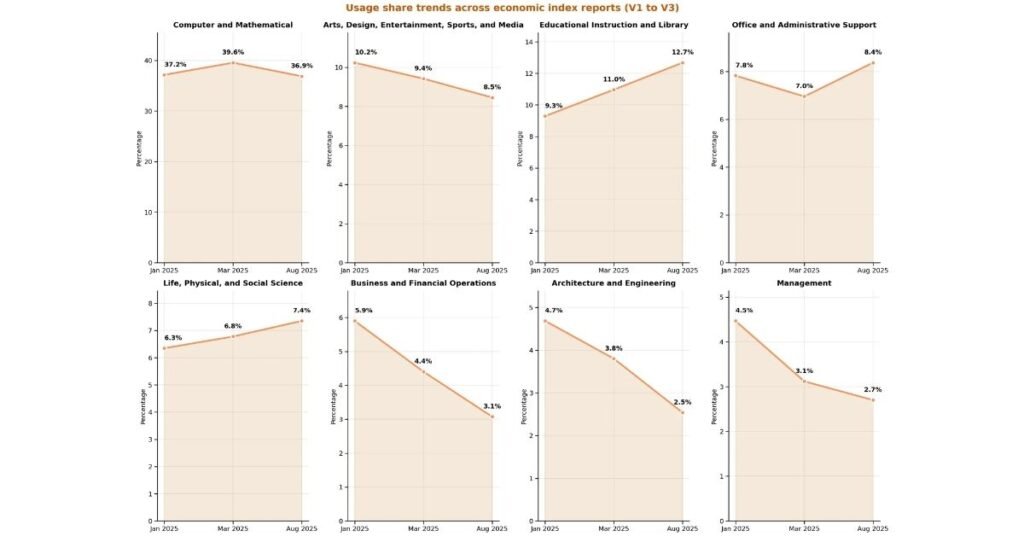
The September report extends this with geographic and enterprise API examinations, offering empirical evidence on AI’s nascent economic effects. By open-sourcing datasets, the Anthropic Economic Index Report fosters collaborative research to inform policy on workforce evolution.
Key Findings on AI Adoption and Job Displacement
The Anthropic Economic Index Report indicates that AI usage at work has doubled to 42% among U.S. employees in 2025 from 20% in 2023, with mid-salary roles in software development and technical writing facing disproportionate impacts.
Task-level automation is evident in routine functions, displacing workers in predictable jobs, though the report cautions that comprehensive long-term displacement predictions remain premature.
CEO Dario Amodei has forecasted up to 20% unemployment in entry-level white-collar positions due to AI’s rapid advancement, emphasizing the need for adaptive strategies.
These findings from the Anthropic Economic Index Report highlight AI’s dual potential for efficiency and disruption, particularly in automatable sectors.
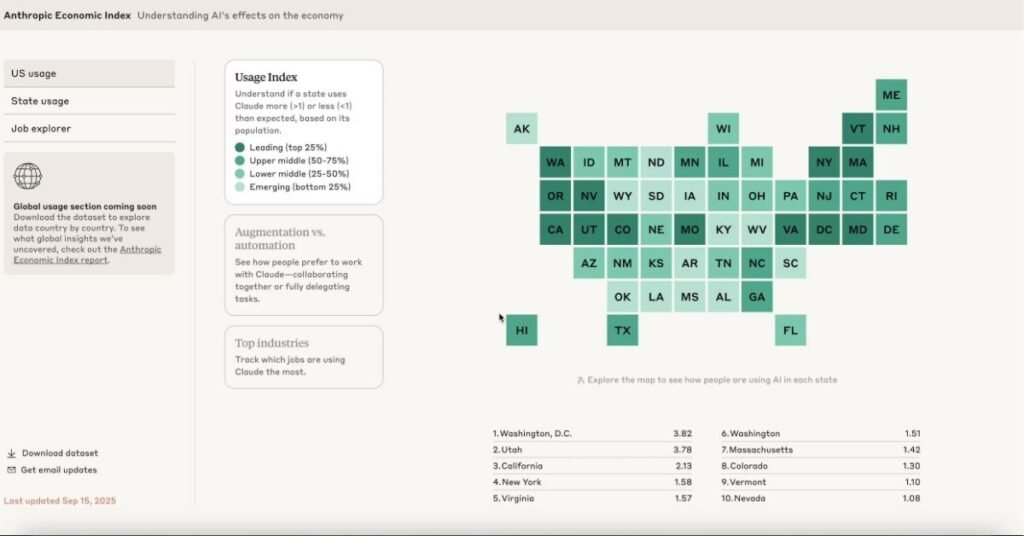
Geographic and Enterprise Disparities in AI Usage
Geographic analysis in the Anthropic Economic Index Report reveals stark disparities, with high-income states like California and New York leading AI adoption, driven by tech hubs favoring coding and financial centers prioritizing analytical tasks.
Per capita usage correlates with economic structures, leaving rural and lower-income areas lagging, potentially widening inequalities. At the enterprise level, a shift toward directive API integrations for automation doubling since early 2025 signals productivity boosts but risks labor market volatility.
The Anthropic Economic Index Report warns that such patterns could exacerbate global divides, as wealthier regions capture AI benefits more readily, underscoring the urgency for inclusive deployment strategies.
Economic Implications and JPMorgan Alignment
The Anthropic Economic Index Report delineates broader economic ramifications, aligning with JPMorgan’s projections of net job gains from AI despite initial disruptions, mirroring electrification’s historical precedent.
Adaptable workers may secure higher wages through AI-enhanced roles, while those in routine tasks face challenges, potentially concentrating benefits in high-adoption economies.
JPMorgan notes a mildly negative correlation between AI intensity and job growth outside tech sectors, with less than 10% of firms using AI regularly as of mid-2025.
The Anthropic Economic Index Report stresses risks of inequality amplification if unaddressed, advocating for policies to distribute productivity gains equitably across the workforce.
Social Media Debates and Public Reactions
On platforms like X, the Anthropic Economic Index Report has ignited debates tying AI automation to surging college graduate unemployment, with users decrying entry-level job scarcity and calling for reskilling amid fears of a “white-collar bloodbath.”
Axios and TechCrunch experts echo worker anxiety, highlighting policy gaps and Anthropic’s advocacy for mitigation, including AI company taxes to fund redistribution.
VentureBeat analyses praise the report’s data-driven transparency but urge collective action to avert upheaval. These reactions underscore the Anthropic Economic Index Report’s catalyst role in public discourse on balancing innovation with social safeguards.
U.S. Army’s Response and Reskilling Initiatives
In response to AI-driven transformations, the U.S. Army announced a new occupational specialty, 49B, focused on AI and machine learning in July 2025, establishing dedicated career paths for enlisted personnel and officers to integrate technology into operations.
This initiative, building on the 2018 AI Task Force, serves as a reskilling model for civilian sectors, emphasizing training in predictive maintenance and data analysis.
Linking to the Anthropic Economic Index Report’s focus on labor adaptation, it promotes augmentation programs and policy frameworks to cushion disruptions, positioning military expertise as a blueprint for broader workforce readiness.
Challenges and Future Outlook from the Report
The Anthropic Economic Index Report identifies key challenges, including ethical dilemmas from job losses and the innovation-inequality tension, necessitating continuous data monitoring as AI advances.
Ethical concerns over displacement parallel calls for transparency in automation. Future updates may inform holiday economic forecasts and international diplomacy, with timelines for policy implementation potentially accelerating by 2026.
The report’s ongoing evolution promises deeper insights into AI’s trajectory, guiding stakeholders toward sustainable integration.
Conclusion
The Anthropic Economic Index Report stands as an indispensable resource for dissecting AI’s influence on job displacement and economic dynamics, leveraging rigorous data to guide policymakers and businesses.
Its revelations on adoption patterns and disparities highlight the imperative for proactive interventions to ensure equitable outcomes.
Ultimately, measures inspired by the Anthropic Economic Index Report could cultivate balanced growth, tempering risks in an AI-centric economy while harnessing its vast potential.

Abdul Basit is a US-based tech writer who covers Apple innovations, Tesla’s EV growth, AI breakthroughs, smartphone trends, and app reviews for global readers.